
Below is given all possible combination of Class B subnetting − Class C SubnetsĬlass C IP addresses are normally assigned to a very small size network because it can only have 254 hosts in a network. Class B IP Addresses can be subnetted the same way as Class A addresses, by borrowing bits from Host bits.

Class B Subnetsīy default, using Classful Networking, 14 bits are used as Network bits providing (2 14) 16384 Networks and (2 16-2) 65534 Hosts.
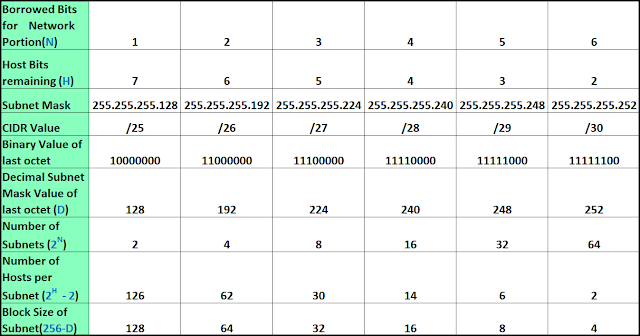
Because these two IP addresses cannot be assigned to hosts, sub-netting cannot be implemented by using more than 30 bits as Network Bits, which provides less than two hosts per subnet.
#Subnetting chart series#
In case of subnetting too, the very first and last IP address of every subnet is used for Subnet Number and Subnet Broadcast IP address respectively. Cheat Sheet Series Prex Length Slash Notation (CIDR) Addresses (Total IPs) Max Available Hosts (Usable IPs) Subnet Length Subnet Mask /32 1 1 0 255.255.255. You can use the IPv4 and IPv6 charts for IP address planning and to convert subnet masks to CIDR and wildcards. Given below is a list of all possible combination of Class A subnets − Subnet Cheat Sheet Quick reference crib sheet for daily subnetting tasks. The Subnet mask is changed accordingly to reflect subnetting. To make more subnet in Class A, bits from Host part are borrowed and the subnet mask is changed accordingly.įor example, if one MSB (Most Significant Bit) is borrowed from host bits of second octet and added to Network address, it creates two Subnets (2 1=2) with (2 23-2) 8388606 Hosts per Subnet. In Class A, only the first octet is used as Network identifier and rest of three octets are used to be assigned to Hosts (i.e. By using subnetting, one single Class A IP address can be used to have smaller sub-networks which provides better network management capabilities. Classful IP addressing does not provide any flexibility of having less number of Hosts per Network or more Networks per IP Class.ĬIDR or Classless Inter Domain Routing provides the flexibility of borrowing bits of Host part of the IP address and using them as Network in Network, called Subnet.
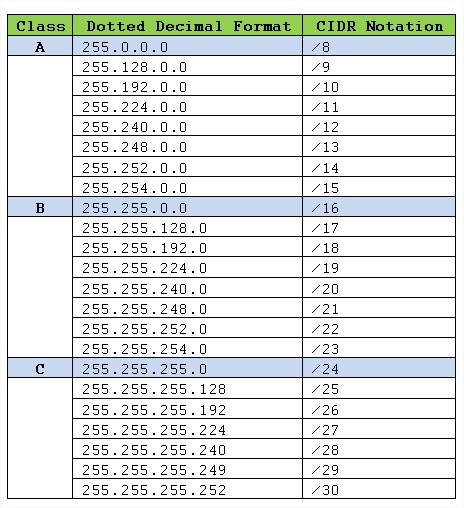
Each IP class is equipped with its own default subnet mask which bounds that IP class to have prefixed number of Networks and prefixed number of Hosts per network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
